Want to share this article?
Subsea Processing Helping Boost Recovery Rates
As producers and E&P companies continue to look for new and innovative ways to cut costs and boost recovery rates, seabed production solutions are becoming increasingly important.
Gas compression and subsea separation technologies in particular, have become extremely useful tools for offshore providers looking to avoid the high costs associated with the use of floating production platforms. With these technologies, producers can transport product directly from subsea to shore; helping improve field economics and optimize production.
It’s estimated that boosted wet tree developments can deliver anywhere from 5% to 20% higher recovery rates compared to dry tree developments. This is rather significant considering the fact that in reservoirs with non-ideal subsurface conditions in terms of porosity in permeability, a very small increase in recovery can translate into nearly $1 billion.
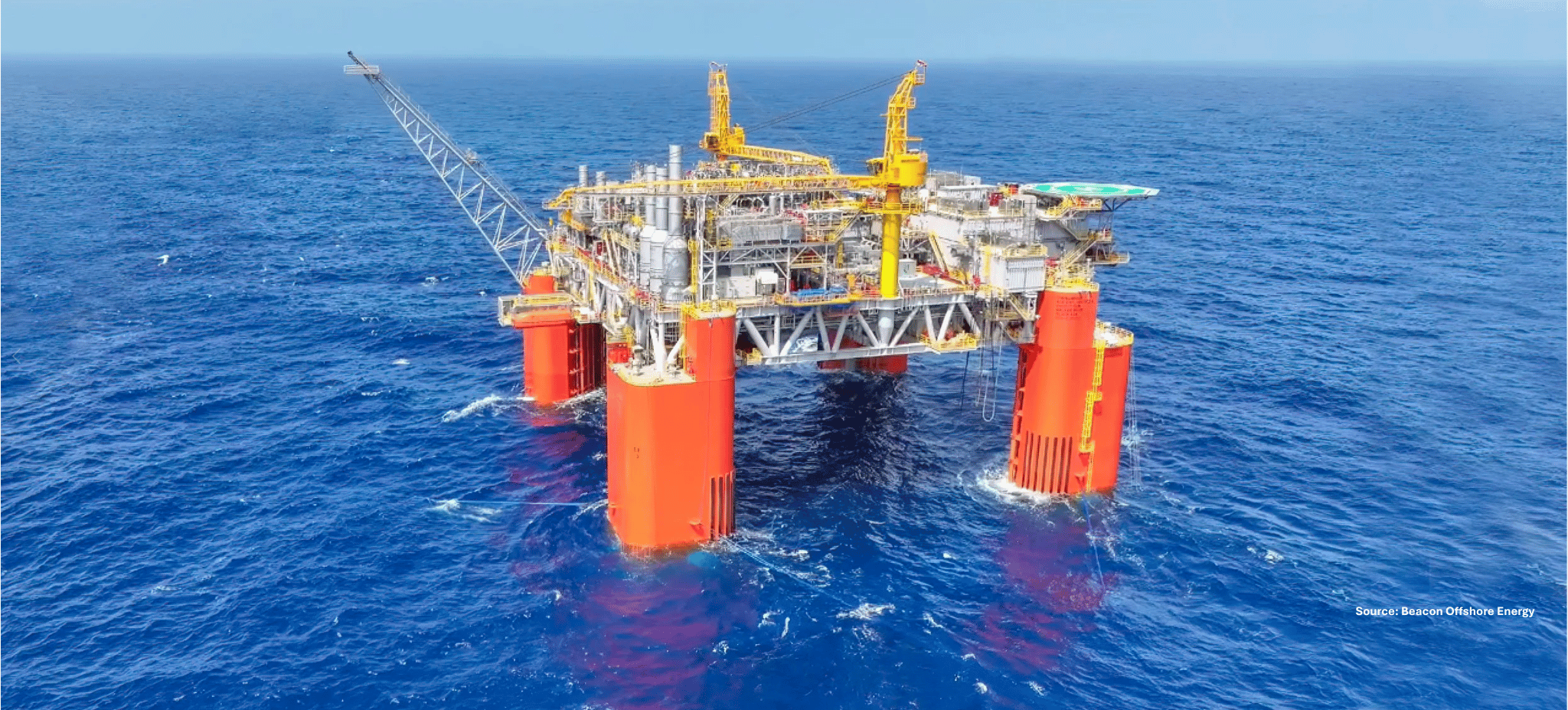
In large part this is due to the fact that wet tree developments include permanent downhole provisions for temperature and pressure monitoring along with provisions for multi-zone completion flow control and hydrate inhibition. Typical wet tree host facilities include semi-submersibles, compliant towers, tension-leg platforms, spars, FPSOs, and floating production units.
Though in the past, flow assurance issues caused by long tie-ins have proved problematic for wet tree systems, low cost submersible hulls and simplified riser/vessel interfaces have made them attractive options in more challenging deepwater formations.
The increased use of subsea separation tools has played a pivotal role in the development of both new and mature oilfields, and with the benefits of wet tree developments becoming more widely understood throughout the oil and gas industry, their use will likely become more commonplace.